an encyclopedia of finite element definitions
Degree 2 Brezzi–Douglas–Fortin–Marini on a quadrilateral
◀ Back to Brezzi–Douglas–Fortin–Marini definition page
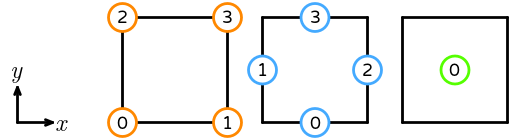
- \(R\) is the reference quadrilateral. The following numbering of the subentities of the reference is used:
- \(\mathcal{V}\) is spanned by: \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle x\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle y\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle y\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x y\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle x y\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x^{2}\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle y^{2}\end{array}\right)\)
- \(\mathcal{L}=\{l_0,...,l_{9}\}\)
- Functionals and basis functions:
\(\displaystyle l_{0}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{0}}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot(1 - s_{0})\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{0}\)
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{0}\) is the normal to facet 0;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
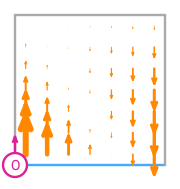
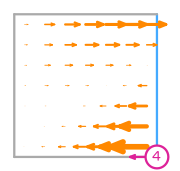
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{0} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 6 x y - 6 x + 3 y^{2} - 7 y + 4\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference element.
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{0}\) is the normal to facet 0;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{0} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 6 x y - 6 x + 3 y^{2} - 7 y + 4\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{1}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{0}}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot(s_{0})\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{0}\)
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{0}\) is the normal to facet 0;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
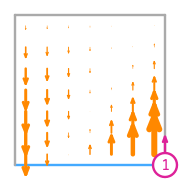
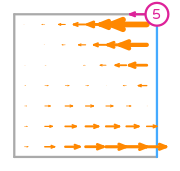
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{1} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle - 6 x y + 6 x + 3 y^{2} - y - 2\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference element.
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{0}\) is the normal to facet 0;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{1} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle - 6 x y + 6 x + 3 y^{2} - y - 2\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{2}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{1}}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot(1 - s_{0})\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{1}\)
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{1}\) is the normal to facet 1;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
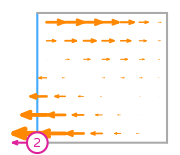
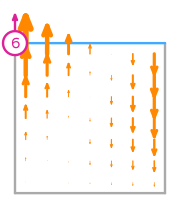
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{2} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - 3 x^{2} - 6 x y + 7 x + 6 y - 4\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference element.
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{1}\) is the normal to facet 1;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{2} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - 3 x^{2} - 6 x y + 7 x + 6 y - 4\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{3}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{1}}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot(s_{0})\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{1}\)
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{1}\) is the normal to facet 1;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
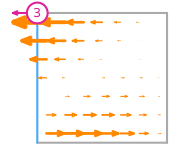
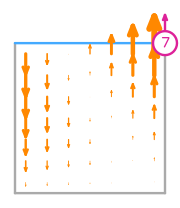
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{3} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - 3 x^{2} + 6 x y + x - 6 y + 2\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference element.
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{1}\) is the normal to facet 1;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{3} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - 3 x^{2} + 6 x y + x - 6 y + 2\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{4}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{2}}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot(1 - s_{0})\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{2}\)
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{2}\) is the normal to facet 2;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{4} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x \left(- 3 x + 6 y - 1\right)\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference element.
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{2}\) is the normal to facet 2;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{4} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x \left(- 3 x + 6 y - 1\right)\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{5}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{2}}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot(s_{0})\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{2}\)
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{2}\) is the normal to facet 2;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{5} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x \left(- 3 x - 6 y + 5\right)\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference element.
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{2}\) is the normal to facet 2;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{5} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x \left(- 3 x - 6 y + 5\right)\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{6}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{3}}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot(1 - s_{0})\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{3}\)
where \(e_{3}\) is the 3rd edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{3}\) is the normal to facet 3;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{3}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{6} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle y \left(- 6 x + 3 y + 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 3 of the reference element.
where \(e_{3}\) is the 3rd edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{3}\) is the normal to facet 3;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{3}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{6} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle y \left(- 6 x + 3 y + 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 3 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{7}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{3}}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot(s_{0})\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{3}\)
where \(e_{3}\) is the 3rd edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{3}\) is the normal to facet 3;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{3}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{7} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle y \left(6 x + 3 y - 5\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 3 of the reference element.
where \(e_{3}\) is the 3rd edge;
\(\hat{\boldsymbol{n}}_{3}\) is the normal to facet 3;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{3}\).
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{7} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle y \left(6 x + 3 y - 5\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 3 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{8}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)\)
where \(R\) is the reference element.
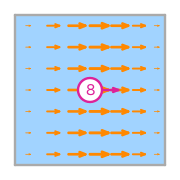
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{8} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 6 x \left(1 - x\right)\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference element.
where \(R\) is the reference element.
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{8} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 6 x \left(1 - x\right)\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference element.
\(\displaystyle l_{9}:\boldsymbol{v}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}\boldsymbol{v}\cdot\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)\)
where \(R\) is the reference element.
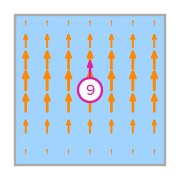
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{9} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 6 y \left(1 - y\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference element.
where \(R\) is the reference element.
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{9} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 6 y \left(1 - y\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference element.