an encyclopedia of finite element definitions
Degree 1 enriched vector Galerkin on a quadrilateral
◀ Back to enriched vector Galerkin definition page
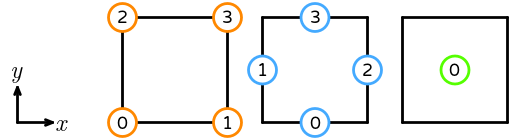
- \(R\) is the reference quadrilateral. The following numbering of the subentities of the reference is used:
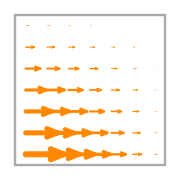
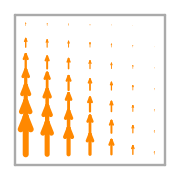
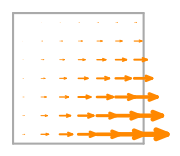
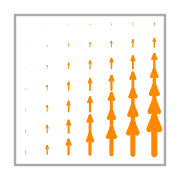
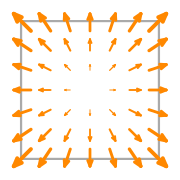
- Basis functions:
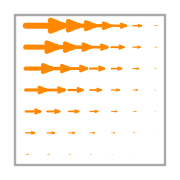
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{0} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x y - x - y + 1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
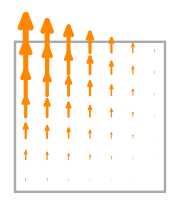
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{1} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle x y - x - y + 1\end{array}\right)\)
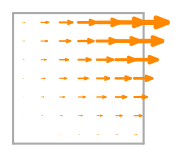
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{2} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x \left(1 - y\right)\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
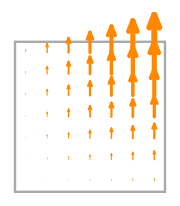
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{3} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle x \left(1 - y\right)\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{4} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle y \left(1 - x\right)\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{5} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle y \left(1 - x\right)\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{6} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle x y\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\phi}_{7} = \left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle x y\end{array}\right)\)